出っ歯(上顎前突)について

出っ歯のお悩みは
外科治療が可能です
上顎の突出感が強い状態は、出っ歯(上顎前突)と称されます。横顔の中顔面部が突出されるため審美的なお悩みを持たれるかたも多く、不正咬合の可能性も高いため当院では治療を推奨しています。患者さん一人ひとりの状態をしっかり検査して、適した治療方法をご提案させていただきます。
こんな場合はご相談ください
- 前歯が出ている
- 上顎が出ている
- 噛み合わせが悪い
- 口周りの見た目が気になる
治療について
ルフォーI型骨切り術(上顎骨切り術)とは
上顎の骨を一部切り離し、適切な位置へ移動させる外科的な治療法です。主に上顎前突や開咬の改善を目的として行われます。手術後は、チタン製または生体吸収性の固定プレートで骨をしっかりと固定し、安定した噛み合わせと顔面バランスを整えます。矯正治療と併用して行われることも多く、骨格からの改善を図る治療法です。


審美面での変化(ガミースマイル・人中短縮・口角挙上など)
上顎の位置を整えることで、ガミースマイル(歯ぐきが見えやすい状態)の改善に加え、人中の長さが短く見える効果が期待できます。また、口角が自然に引き上がり、笑顔の印象が明るくなるケースもあります。一方で、上顎を後退させることで口唇がやや薄く見えることがあり、患者さんによってはメリットにもデメリットにもなり得ます。こうした変化を踏まえ、事前に顔貌のシミュレーションを行い、バランスを確認してから治療を進めます。
ルフォーI型骨切り術における手術時の流れ
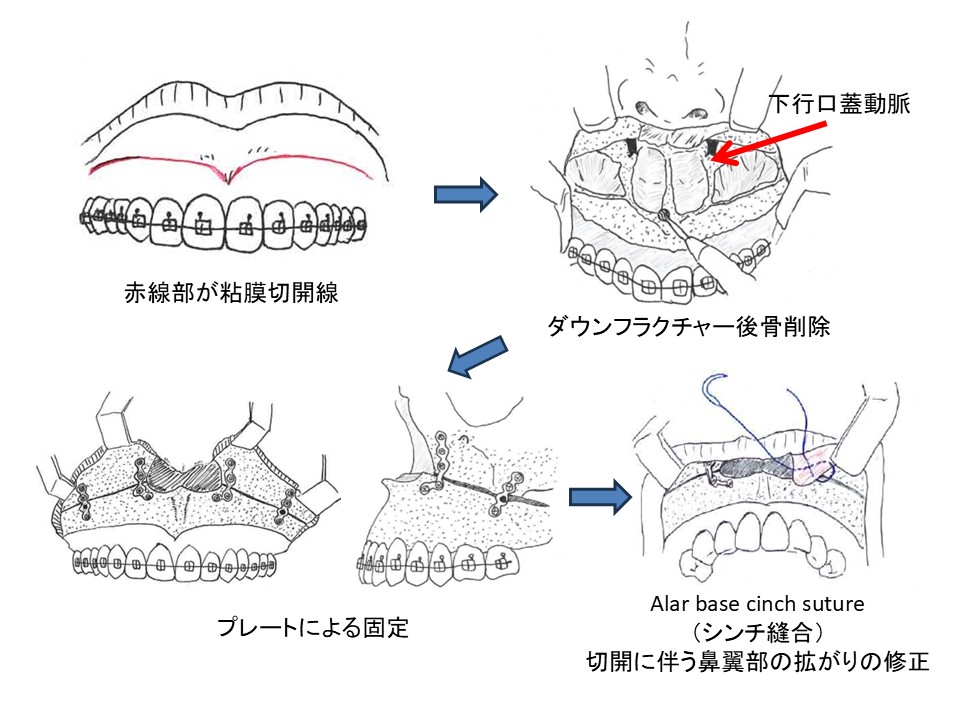
01 粘膜切開線(口腔内切開)
上顎の歯ぐきの上(前庭部)に、左右にわたって粘膜切開を行い、骨の表面が見えるように粘膜骨膜弁を剥離して術野を確保します。口の中からアプローチするため、基本的に顔面皮膚に切開線は残りません。
02 ダウンフラクチャー後の骨削除(干渉部のトリミング)
骨切り(上顎骨を可動化するための骨切り操作)を行って上顎骨を「動かせる状態」にした後、**ダウンフラクチャー(上顎骨骨片を下方へ可動させて展開する操作)**を行います。 そのうえで、予定した位置に上顎骨を移動させる際に邪魔になる骨(干渉部)がある場合は、**骨削除(トリミング)**を行い、骨片が無理なく所定の位置に収まるよう調整します。後方移動などでは上顎結節周囲の干渉調整が説明されることが多いです。
03 プレートによる固定
移動後の上顎骨が計画位置に安定していることを確認したら、チタンミニプレートとスクリューなどで骨片を固定します。固定部位は術式・移動量などで変わりますが、梨状口縁部や頬骨下稜部周辺などに複数箇所固定する説明が一般的です。
04 切開に伴う鼻翼部の拡がりの修正
口腔前庭からの切開・剥離により、術後に鼻翼基部(小鼻の付け根)が外側へ広がる方向の変化が出ることがあるため、必要に応じてAlar base cinch suture(シンチ縫合)を行います。これは、鼻翼基部周囲(鼻の筋・軟部組織)を内側へ寄せるように縫合して、鼻翼の拡がりを抑える/修正する目的で行われます。
費用
料金表
| 初診料 | 無料 |
|---|---|
| 診察料 | 1,100円 |
| 当日キャンセル料 | 5,500円 |
※表示金額は全て税込みです
| ルフォーI型骨切り術(上顎骨切り術) | 1,540,000円 |
|---|
※表示金額は全て税込みです
お支払方法

- 現金
- 現金でのお支払い

- クレジットカード
- VISA/JCB/
Mastercard/など

- デンタルローン
- 低金利分割払いでの
お支払い
医療費控除について
1年間(1月1日~12月31日)に10万円以上の医療費を支払った場合は、医療費控除によって一定の金額の所得控除を受けることができます。ご自身の支払いに限らず、生計を共にするご家族が支払った医療費も対象となります。詳しくは国税庁のホームページをご覧ください。
モニター募集

治療をお得に受けることができる
モニター制度を導入しております
当院では施術の内容や術後の経過を掲載するモニター制度を設けており、施術をお得に受けることができます。モニターは顔出しなしですが、場合によっては動画撮影をお願いすることはございます。モニター制度をご利用の際には条件などがありますので、気になるかたは一度当院までお問い合わせください。
注意点・リスク・副作用
・術後は内出血、腫れ、しびれ、知覚異常などが生じることがあります。
・術後数週間から数ヵ月の間、食事制限をしていただく必要があります。


